
What is the difference between Source & Medium in Google Analytics (GA4)?
Source and Medium in Google Analytics is something that even the best digital marketers get mixed up sometimes. Google’s support and guideline are as normal a bit washy and wordy, so we thought we’d try and explain it simply.
This article was originally written for Universal Analytics and has now been updated for GA4
Source vs Medium in GA4
Source is where your website’s traffic comes from (individual websites, Google, Facebook etc).
Medium is how it got there (organic traffic, paid traffic, referral etc).
People like analogies (apparently), so here’s one:
- Think of a journey. The Source would be where you came from, the Medium, is the method of Transport.
or
- The Source would be the train station, the Medium would be a train (now the above image makes sense)
Before we break it down further, I’m going to add another definition into the mix… Channel. We’ve written an article on ‘What are Channels in Google Analytics & How to Change Them?’, so have a read of that if you want to know more, but essentially Channels are named groupings of Source & Medium.
So, now you’ve had the simple explanation of what Source and Medium are, let’s go into them further.
What is Source in GA4
The Source in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is where your website’s traffic comes from, or as Google says, it’s the origin of your traffic. Your traffic has to come from somewhere, whether that’s people visiting your site from search engines, social media sites, or another website. When there is no data on the original website, the source is known as Direct. This is when someone types your URL into a browser, clicks a bookmark, or comes from an offline tool or document on their computer (if tracking has not been set up). If it’s not direct, it should be the name of a site.
In GA4, the processing and display of Source information might differ slightly from Universal Analytics. GA4 uses event-based data collection, which can result in more flexible and detailed tracking. This means that while the fundamental concept of Source remains the same, the data might be represented differently in reports, with more granularity and contextual insights available.
What is Medium in GA4
Medium in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) represents how your website’s traffic arrived at your site. Google calls it the general category of the source. For example, the Source of your traffic might be Google, but the Medium could be Organic, CPC, Display, or Referral.
There are some core categories within Medium:
- Organic Traffic (non-paid traffic from search engines)
- CPC/PPC (paid traffic from search engines)
- Referral (a link from another website)
- Email (link from an online email tool such as Hotmail or Gmail)
- Social (link from a social media site)
- None (direct traffic)
In GA4, the categorisation and reporting of Medium might have nuanced differences compared to Universal Analytics. GA4’s event-based data model allows for more detailed and flexible tracking, which means the way Medium data is processed and displayed can provide more contextual insights and granularity.
This could lead to slightly different representations in reports, so it’s important to review GA4-specific documentation and configurations to fully understand how Medium is tracked and reported in GA4.
Can you create your own Source and Medium?
You can create your own Source and Medium by adding parameters to some of the links arriving at your site which will override the existing Source/Medium. This isn’t possible to do it on all links. So Organic links from Google will always be Source = Google, Medium = Organic. However, if for instance, you have an email campaign that includes links to your site, normally this would either be shown as:
- Source = Gmail, Medium = Email
- Source = Direct, Medium = (none)
- Source = Hotmail, Medium = Email
This doesn’t tell you that the source was actually your Newsletter.
So, in this case, you would build a Campaign URL which creates a parameter at the end of your URL which changes the Source/Medium in Google Analytics. You can do this at https://ga-dev-tools.google/ga4/campaign-url-builder/. It’s a really simple tool where you enter in your URL, tell it what the Source and Medium should be, and it will give you the URL to use. You can even add Campaign Name, Campaign Term and Campaign Content.
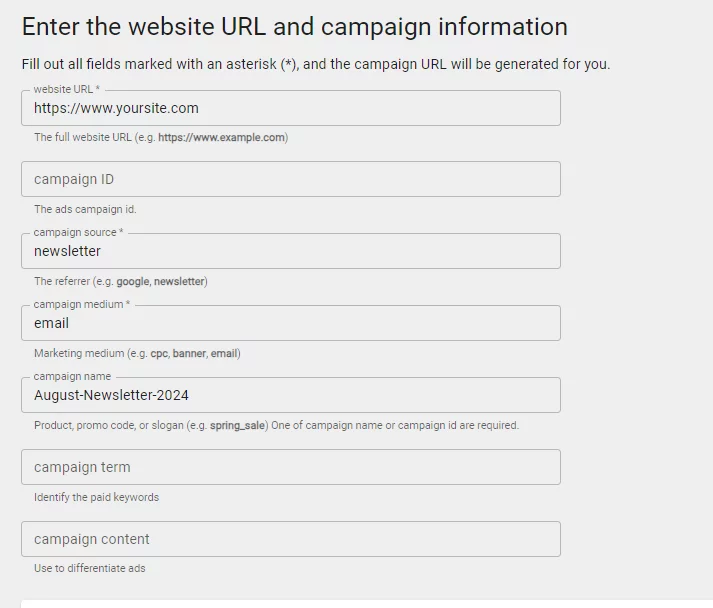

The above will generate the URL https://www.yoursite.com/?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=August-Newsletter-2019
When this link is clicked, it will change the Source/Medium in Google Analytics
 Reporting in GA4: In GA4, these custom parameters will be processed and displayed in your reports, but with more flexibility and potentially different categorization compared to Universal Analytics. GA4’s event-based data model allows for more detailed tracking and insights, so you might see these parameters represented differently in your reports.
Reporting in GA4: In GA4, these custom parameters will be processed and displayed in your reports, but with more flexibility and potentially different categorization compared to Universal Analytics. GA4’s event-based data model allows for more detailed tracking and insights, so you might see these parameters represented differently in your reports.
Again, you won’t be able to use this on all traffic coming into the site, only the URLs that you control people clicking on, i.e. not organic traffic, not naturally earned links etc.
One note about this tool. Source and Medium are case sensitive, so be careful; ‘newsletter’, ‘Newsletter’ and ‘NewsLetter’ would be classed as different sources.
Can we help you?
We hope you’ve found this article useful, and if you would like to find out about Channels in Google Analytics, please read this article. Propellernet offers Google Analytics training, so if you would like to learn more face to face, please contact us. If you are concerned that your Google Analytics account, we can perform a full Google Analytics Audit or for anything else, checkout our range of Analytics Services



